3 June 2022
Exposition sur l’énergie au MUS’X
LA RECHERCHE D’AUJOURD’HUI POUR L’ENERGIE DE DEMAIN
A l’heure de la hausse de la concentration de dioxyde de carbone (CO²) dans l’atmosphère (413,2 parties par million en 2020), de la hausse (...)
Home > News

The electric field-induced modifications of the spatial distribution of photoelectrons, photoholes, and electronic spins in optically pumped p + GaAs are investigated using a polarized luminescence imaging microscopy. At low pump intensity, application of an electric field reveals the tail of charge and spin density of drifting electrons. These tails disappear when the pump intensity is increased since a slight differential drift of photoelectrons and photoholes causes the buildup of a strong internal electric field. Spatial separation of photoholes and photoelectrons is very weak so that photoholes drift in the same direction as photoelectrons, thus exhibiting a negative effective mobility. In contrast, for a zero electric field, no significant ambipolar diffusive effects are found in the same sample.
Plus d’information

3 June 2022
LA RECHERCHE D’AUJOURD’HUI POUR L’ENERGIE DE DEMAIN
A l’heure de la hausse de la concentration de dioxyde de carbone (CO²) dans l’atmosphère (413,2 parties par million en 2020), de la hausse (...)
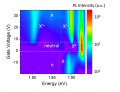
24 May 2022
A recently published work from the “Electrons Photons Surfaces” group explores the valley degree of freedom of charged excitons in atomically thin semiconductors.
Transition metal (...)
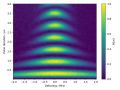
8 April 2022
The QCMX Lab of the EPS group is a partner of the PEPR project ROBUSTSUPERQ (Quantum Plan). This project aims at accelerating French R&D on superconducting and hybrid qubits protected by (...)
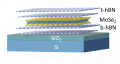
13 September 2021
A recently published work from the “Electrons Photons Surfaces” group explores the peculiar transport properties of excitons in novel, atomically thin 2D semiconductors. A polarized (...)
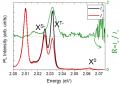
13 September 2021
One of the most promising properties of novel 2D semiconductors based on transition metal dichalcogenides are related to the possibility of manipulating the spin and valley (momentum) degree of (...)
Page(s) : <