Contact : F. Ozanam
Participants : F. Ozanam, M. Rosso, C. Henry de Villeneuve
Research engineer : N. T. Phung
Lithium-ion batteries are among the best current solutions for storing electrical energy. The replacement of carbon which is currently used in negative electrodes by silicon would further improve their performance. However, silicon undergoes very significant volume variations during charge/discharge cycles, yielding rapid battery degradation.
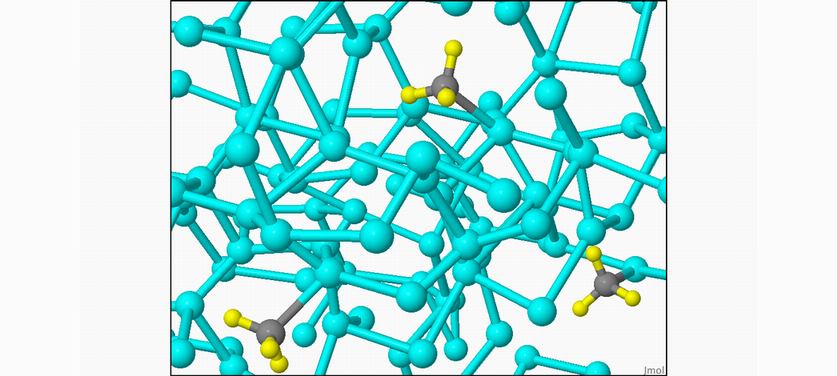
We are working on a new material derived from silicon, methylated amorphous silicon (Fig.1), which has the advantage of better accommodating volume variations. Our studies, carried out on thin layer electrodes (thickness ≤ 400 nm), show that this new material has a much better stability upon cycling (about 80% of the initial capacity preserved for more than one thousand cycles) and a faradic efficiency - ratio between the released charge and the stored charge - very close to unity.
Since 2022, in collaboration with the Solid Mechanics Laboratory of Ecole Polytechnique, we have been studying the coupling between mechanical stress and the silicon lithiation/delithiation process.
Fig. 1 : (a) Structure at the atomic scale of methylated amorphous silicon : the blue-cyan spheres represent the silicon atoms, the gray and the yellow spheres represent the methyl groups (1 carbon bonded to 3 hydrogens and to 1 silicon).
Recent theses :
Yue Feng (2021), "Lithiation of Methylated Amorphous Silicon"
https://theses.hal.science/tel-03696528v1/document
Ngoc Tram Phung (2023), "Methylated amorphous silicon for Li-ion batteries"
https://theses.hal.science/tel-04532178v1/document
Collaborations : IRCP (Chimie ParisTech), ICMPE (Thiais), LMS (Ecole Polytechnique).
Funding : E4C, DGA, chaire Total-DTER, chaire EDF-Développement durable.
Recent publications :
[Feng2022b] ToF-SIMS Li depth profiling of pure and methylated amorphous silicon electrodes after their partial lithiation, Feng, Y., Koo, B. M., Seyeux, A., Światowska, J., Henry de Villeneuve, C., Rosso, M., Ozanam, F., ACS APPL. MATER. INTERFACES 14 (2022) 35716-35725
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c08203
[Feng2022a] Controlling homogeneity of the first lithiation in methylated amorphous silicon, Feng, Y., Cheriet, A., Panagopoulou, M., CHenry-de-Villeneuve, C., Rosso, M., Ozanam, F., ELECTROCHIM. ACTA 403 (2022) 139655.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139655
[Feng2019] Lithiation of pure and methylated amorphous silicon : monitoring by operando optical microscopy and ex situ atomic force microscopy, Feng, Y., Ngo, T.-D.-T., Panagopoulou, M., Cheriet, A., Koo, B. M., Henry-de-Villeneuve, C., Rosso, M., Ozanam, F., ELECTROCHIM. ACTA 302 (2019) 249-258.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.02.016
[Koo2018] Lithiation Mechanism of Methylated Amorphous Silicon Unveiled by Operando ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy, Koo, B. M., Dalla Corte, D. A., Chazalviel, J.-N., Maroun, F., Rosso, M., Ozanam, F., ADVANCED ENERGY MATERIALS 8 (2018) 702568
https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201702568