Contact : Yves Lassailly
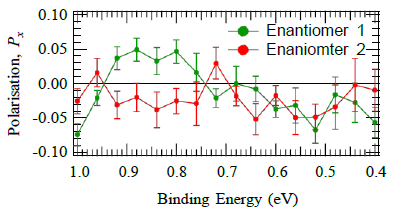
In collaboration with University of Manchester (N. Lewis and E. Seddon) and University of Nebraska (T.J. Gay group), we investigate the spin polarization on semi-conductor and metal surfaces due both the Rashba effect and the lack of inversion symmetry of the surface lattice. Band structure calculations on chiral surfaces predict that eigenstates at specific k directions have components of the spin polarization vector P which are strongly dependent on the chirality of the surface. Using the spin-resolved UV photoemission equipment on APE synchrotron beamline in Elettra, we have shown that a weak localized surface state of the Si(110)-16x2 reconstructed chiral surfaces has a small non-zero longitudinal spin polarization (Px of 5%) unlike achiral surfaces.